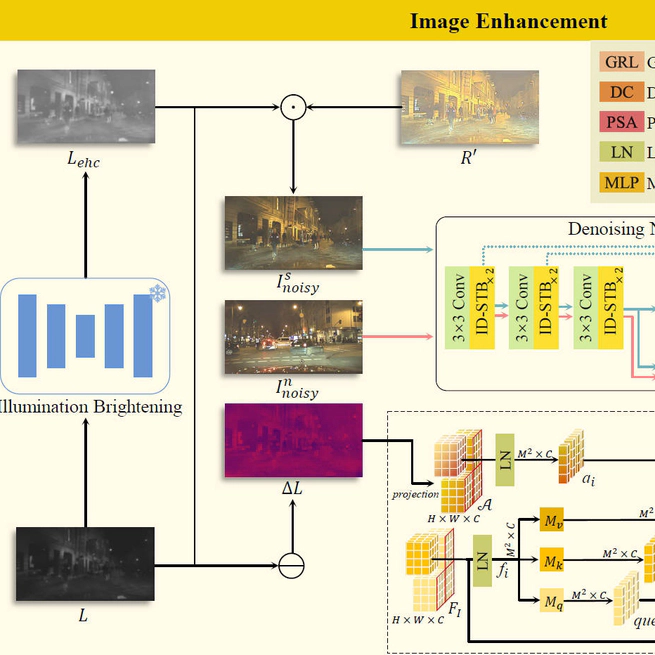
Abstract Detecting vulnerable road users (VRUs) at night presents significant challenges. Numerous methods rely heavily on annotations, yet the low visibility of nighttime images poses difficulties for labeling. To obviate the need for nighttime annotations, unsupervised domain adaptation manifests as a viable solution. However, existing approaches often focus solely on semantic-level domain shifts, neglecting the pixel-level discrepancies due to inherent degradations in the night domain, which can significantly impair machine vision. This oversight limits the effectiveness of nighttime VRU detection. To this end, TripleA, an unsupervised domain adaptation framework is introduced to achieve nighttime VRU detection. Realized through a crucial triple alignment, TripleA first aligns the distributions of the labeled daytime domain with the unlabeled nighttime domain. Then, the degraded image is enhanced in terms of illumination and noise. We present an illumination difference-aware denoising network to address the intractable noise and enable selfsupervised learning through a meticulously designed exchange-recombination strategy, which is integrated into a novel pseudosupervised attention to achieve noise distribution alignment. To further enhance the capabilities of the denoising network under real-world scenarios, we introduce degradation alignment to enforce domain-invariant degradation encoding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework achieves superior performance in nighttime VRU detection without relying on nighttime annotations. My Role I am the first author of the study and I completed all the steps of conceptualizing the experiment, conducting the experiment and writing the paper. Research Content VRUs in traffic surveillance camera data during the daytime were labeled. An unsupervised domain adaptation framework was proposed for nighttime VRU detection using only daytime annotations, reducing the cost of manually labeling challenging nighttime data An illumination difference-aware denoising network was designed to suppress noise that is coupled with illumination in nighttime images, the network can be trained in a self-supervised manner A paper manuscript was authored and it is currently under review by IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
Apr 28, 2024

Overview This project is oriented to the needs of urban municipal road traffic infrastructure maintenance, to carry out research on urban municipal road asset verification technology and urban municipal road pavement damage detection technology, and to select a typical urban municipal road section in Qiaokou District, Wuhan City, to carry out demonstration applications. My Role I am the student leader, responsible for the development of road damage detection algorithms, project schedule control, and also responsible for the coordination of all parties involved. Research Content A road damage dataset was constructed, which contains the physical properties (width, length, depth) of road damage. The YOLOv5 architecture was enhanced by integrating additional regression heads to predict the physical properties of detected road damage. An integral transform function (CDT) was developed to address the long-tailed distribution problem in values of regression variables. The model was deployed on sanitation vehicles in Qiaokou District, Wuhan, China, to validate the algorithm’s robustness in real-world scenarios.
May 1, 2023
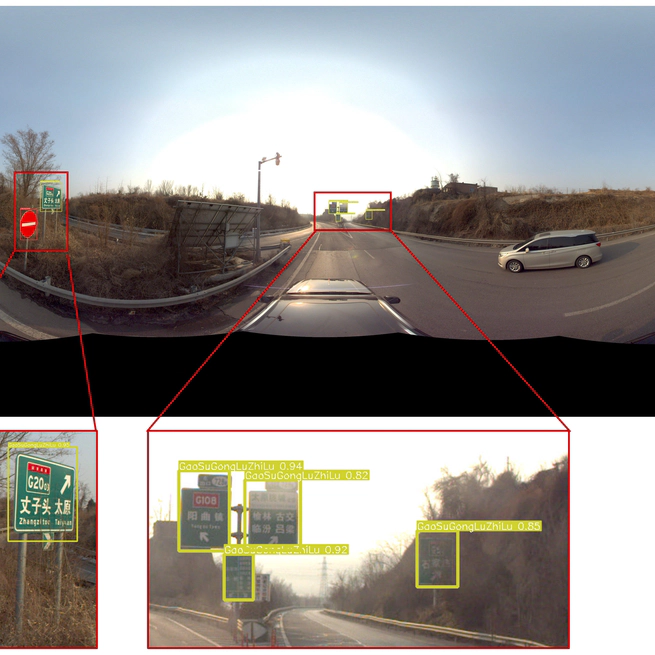
Overview Highway assets are widely distributed, and the existing asset inventory mainly relies on manpower, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive, and cannot realize high-frequency inspection. To address the above problems, this study develops automatic inspection methods for different highway asset types based on multi-source data (vehicle-mounted panoramic images, inclined photogrammetry and LIDAR point clouds) and constructs an asset sample database, which realizes automatic inspection of highway assets and rapid updating of information. My Role I am responsible for cleaning the collected panoramic images and then labeling the highway traffic signage in the images using a semi-automatic approach. Research Content A semi-automatic annotation of highway traffic signage was conducted, resulting in a panoramic image dataset A detection model for highway traffic signage was developed.
Jan 1, 2023

Overview In order to better understand urban form, this study qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed the spatial patterns of street network patterns in 1,321 cities in China, and explored the main factors affecting street network patterns in combination with land cover types and topographic data. The results of this study won the 1st prize in Esri-Cup Chinese College Students GIS Software Development Contest. My Role I was the team leader, responsible for the overall planning of the project. I was involved in data preprocessing, qualitative and quantitative calculations of the street network, and thematic and graphic production. Research Content The street network patterns across 1,321 built-up areas in China were mapped and analyzed using orientation entropy and rose diagrams. The spatial autoregressive models were employed to quantitatively understand the relationship between street network patterns and various landscape factors. An interactive visualization of analysis results was implemented using ArcGIS StoryMaps.
Sep 23, 2021